[导读] 作者:慧海拾穗
原发性中枢神经系统肿瘤的免疫组化标记物研究进展(一)
原发性中枢神经系统肿瘤的免疫组化标记物研究进展(二)
Meningioma Subtypes Associated With Germline Mutations | 与胚系突变相关的脑膜瘤亚型 |
The combination of cytogenetic and mutational profiling of meningiomas has revealed a strong association of genomic signatures with several unique histologic growth patterns. The presence of chromosomal polysomies in angiomatous meningiomas, NF2 deficiency in fibrous meningiomas, KLF4/TRAF7 mutations in secretory meningiomas, and multiple broad losses in higher grade meningiomas all require molecular testing to definitively assess. The discovery of somatostatin receptor 2A (SSTR2A) expression in meningiomas has proved a useful adjunct to distinguish meningiomas from histologic mimics; however, until only recently have subtype specific markers been identified for a subset of higher grade meningiomas. | 脑膜瘤的细胞遗传学和突变分析揭示了基因组特征与几种独特的组织学生长模式之间的紧密联系。血管瘤型脑膜瘤中染色体多组分的存在,纤维型脑膜瘤中NF2的缺陷,分泌型脑膜瘤中KLF4/TRAF7的突变,以及高级别脑膜瘤中的多发性广泛缺失都需要分子检测来明确评估。生长抑素受体2A(SSTR2A)在脑膜瘤中的表达证实是区分脑膜瘤和组织学类似脑膜瘤的一个有用的辅助手段;然而,直到最近才发现高级别脑膜瘤亚型特异性标记物。 |
Clear Cell Meningioma | 透明细胞脑膜瘤 |
Clear cell meningiomas represent an extremely rare variant of meningiomas with an increased rate of occurrence commensurate with WHO grade II designation. Descriptions of this tumor type are largely confined to small case series; however, these tumors occur most often in children and young adults with a predilection for the cerebellopontine angle and spinal cord. | 透明细胞脑膜瘤是一种极为少见的脑膜瘤,组织学相当于WHO Ⅱ级。对这种类型肿瘤的描述大多局限于小病例报道;然而,这些肿瘤大多发生于儿童和年轻成人,他们更喜欢小脑桥脑角和脊髓。 |
Histologically, the tumors show epithelioid cell morphology with prominent cytoplasmic clearing and distinctive “blocky” interstitial and perivascular deposits of collagen (Fig. 5A). Other characteristic features of meningioma, including whorl formation and psammoma bodies, are usually absent. As with other meningioma variants, tumor cells routinely stain with both EMA and SSTR2A. | 组织学上,肿瘤呈上皮样细胞形态,胞质明显透亮,间质和血管周围胶原沉积呈明显“块状”(图5A)。脑膜瘤的其他特征性特征,包括漩涡状和砂粒体,通常是缺乏的。与其他脑膜瘤亚型一样,肿瘤细胞通常表达EMA和SSTR2A。 |
Studies investigating familial forms of disease revealed an association with SMARCE1 loss function. SMARCE1 is a member of the SWI/SNF chromatin remodeling complex whose loss is implicated in a subset of cases of Coffin Siris syndrome. Subsequent studies have demonstrated strict correlation between SMARCE1 loss and clear cell meningioma histology (Fig. 5B). Importantly, tumors showing focal clear cell change do not exhibit loss of SMARCE1 by immunohistochemistry. | 调查家族性疾病的研究表明,SMARCE1功能缺失与疾病有关。SMARCE1是SWI/SNF染色质重塑复合物的成员,其丢失与部分Coffin-Siris综合征有关。随后的研究表明SMARCE1缺失与透明细胞脑膜瘤的组织学密切相关(图5B)。重要的是,免疫组化显示局灶性透明细胞改变的肿瘤不会出现SMARCE1的缺失。 |
Rhabdoid Meningioma | 横纹肌样脑膜瘤 |
These tumors constitute a subset of anaplastic meningiomas (WHO grade III), often showing overt features of malignancy and an aggressive clinical course. They are characterized by a preponderance of cells with classic rhabdoid morphology (round cells possessing an eccentric nucleus with open chromatin and a single prominent nucleolus and a dense eosinophilic cytoplasmic inclusion) and high mitotic rate (Fig. 5C). Immunohistochemistry for EMA and SSTR2A is usually positive, and SMARCB1 expression is retained. | 这些肿瘤构成间变性脑膜瘤(WHOⅢ级)的一个亚组,常表现出明显的恶性特征和侵袭性临床过程。其特征是具有典型横纹肌样形态的细胞明显(圆形细胞具有偏心的细胞核,染色质开放,单个突出的核仁和致密的嗜酸性胞质包涵体)和大量核分裂象(图5C)。免疫组化检测EMA和SSTR2A通常为阳性,SMARCB1的表达保留。 |
Comprehensive genomic analysis of a large cohort of rhabdoid meningiomas and meningiomas with focal rhabdoid features uncovered a novel association between BAP1 (BRCA-1 associated protein 1) deficiency and aggressive clinical course. Tumors with homozygous inactivating mutations or deletions show loss of staining for BAP1 (Fig. 5D). Furthermore, a subset of patients showed germline BAP1 mutations, placing rhabdoid meningiomas within the BAP1 cancer predisposition syndrome. Patients with tumors showing BAP1 loss of expression, therefore, should be referred for germline testing. | 大规模对横纹肌样脑膜瘤和具有局灶性横纹肌样特征的脑膜瘤的综合基因组分析揭示了BAP1(BRCA-1相关蛋白1)缺乏与侵袭性临床进程之间的新联系。纯合子失活突变或缺失的肿瘤显示BAP1染色缺失(图5D)。此外,一部分患者表现出胚系BAP1突变,将横纹肌样脑膜瘤归类于BAP1癌症易感综合征中。因此,有BAP1表达缺失的肿瘤患者应进行胚系检测。 |
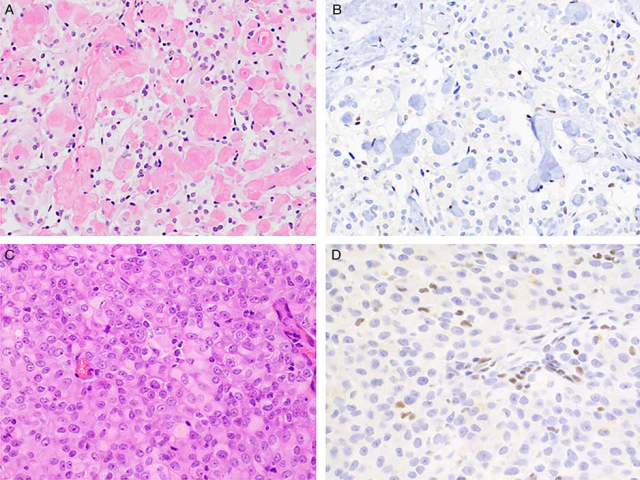 FIGURE 5. Meningioma subtypes associated with germline syndromes. A, Clear cell meningiomas contain epithelioid cells with clear or palely eosinophilic cytoplasm and prominent interstitial blocky collagen. Immunohistochemistry for SMARCE1 is consistently negative in both sporadic and familial examples (B). C, Rhabdoid meningiomas possess a dominant component of rhabdoid cells with abundant, dense eosinophilic cytoplasm and eccentric nuclei with prominent nucleoli. D, BAP1 staining is lost in a subset of tumors and may indicate the presence of BAP1 cancer predisposition syndrome. FIGURE 5. Meningioma subtypes associated with germline syndromes. A, Clear cell meningiomas contain epithelioid cells with clear or palely eosinophilic cytoplasm and prominent interstitial blocky collagen. Immunohistochemistry for SMARCE1 is consistently negative in both sporadic and familial examples (B). C, Rhabdoid meningiomas possess a dominant component of rhabdoid cells with abundant, dense eosinophilic cytoplasm and eccentric nuclei with prominent nucleoli. D, BAP1 staining is lost in a subset of tumors and may indicate the presence of BAP1 cancer predisposition syndrome.
图5 与胚系综合征相关的脑膜瘤亚型:透明细胞脑膜瘤含有上皮样细胞,嗜酸性胞质透亮或淡染,间质有明显的块状胶原(A);在散发性和家族性病例中,免疫组化检测SMARCE1均呈阴性(B)。横纹肌样脑膜瘤以横纹肌样细胞为主,胞质丰富、致密,核偏位、核仁突出(C)。在一部分肿瘤中BAP1表达缺失,可能提示BAP1癌症易感综合征的存在。 |
【参考文献】
[1] Advances in Diagnostic Immunohistochemistry for Primary Tumors of the Central Nervous System.Adv Anat Pathol,2019.












共0条评论