[导读] 作者:詹媛 江西省肿瘤医院,病理科,南昌,330029)
摘要
目的 研究上皮样血管内皮细胞瘤(Epithelioid haemangioendothelioma,EHE)的临床表现、病理学特征及诊断、鉴别诊断。
方法 对我院诊治的4例上皮样血管内皮细胞瘤手术标本进行临床资料收集、光镜观察及免疫组化染色。
结果 4例均为女性患者,年龄30~62岁。
镜下:肿瘤细胞成条索状、巢团状排列,细胞圆形或多角形,胞浆嗜酸性且有空泡形成,核分裂象少见,间质呈软骨样或红染玻璃样并常伴有新旧不等的出血及炎细胞浸润。免疫组化:肿瘤细胞CD34(+)、CD31(+)、FⅧ(+)、Ki-67(+,<10%) 。
结论 EHE是较为罕见的低度恶性肿瘤,主要依据病理学和免疫组化进行诊断。早期发现、局部手术扩大切除和结合放疗为主要治疗手段,有少数患者发生远处转移,因此熟悉EHE临床及病理特征对明确诊断具有重要意义。
上皮样血管内皮细胞瘤 ( epithelioid haemangioendothelioma,EHE) 亦称为组织细胞样血管内皮瘤,多见于成年女性,可发生于肝脏、皮肤、肺、淋巴结等全身多部位[1]。肿瘤由排列成巢的上皮样或组织细胞样内皮细胞构成,具有特殊的玻璃样或软骨样间质成分。EHE是一种以血管为中心的中间型肿瘤,具有转移潜能[2]。因此我们搜集4 例EHE患者的临床资料,共同讨论EHE临床表现、及其预后与病理组织学特点之间的关系。
1 材料与方法
1.1 临床资料
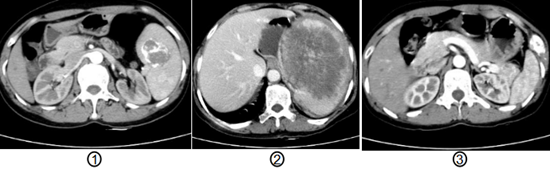
例1 患者,女性,40岁。2013年6月因左上腹部间断性疼痛4月余入院。腹部CT(图)检查时发现脾脏体积增大,内见不规则混杂密度肿块影。最大层面约4.5cm×4.0cm。边缘不清,内见钙质密度影。诊断:脾脏良性病变,错构瘤可能。实验室检查 WBC:3.9×109/L,HGB:104 g/l,CA199:27.62 u/ml,TAM:102 u/ml。
例2 患者,女性,62岁。2014年8月因上腹部隐痛不适2月入院。腹部CT(图)提示脾脏巨大软组织肿块,大小约为11cm×15.3cm。内部密度不均,见低密度坏死及不规则钙化灶。诊断:脾脏占位性病变,考虑恶性肿瘤,血管肉瘤可能。实验室检查 RBC:3.44×1012/L,WBC:20.74×109/L,Plt:467×109/L。患者曾于1994年做过卵巢癌切除手术,术后恢复良好。
例3 患者,女性,44岁。2014年5月因肿块并疼痛半年入院。患者2013年底发现左前胸可扪及枣大包块,触之稍痛。未给予治疗后肿块逐渐增大,遂入院检查。胸部CT(图)发现左第9肋骨轻度膨胀性骨质破坏伴软组织影形成。诊断:考虑骨转移瘤可能性。同月于我院胸外科行“肋骨肿块切除术”。
例4 患者,女性,30岁。2014年7月因颏部肿块1年入院。肿块大小约2cm×2cm,质中,不易推动。彩超检查发现右颏部探及大小43mm×17mm等回声肿物,边界不清楚,形态不规则,内探及丰富血管信号。诊断:实性肿物,不排外恶性可能。
1.2 方法 将组织切开置于10%中性福尔马林中固定。经常规制片(脱水、包埋、切片、染色)后光镜观察。采用Max Vision染色法对组织进行免疫组化标记,所用抗体为CD34、CD31、FⅧ、Ki-67 。抗体试剂盒购自于福建迈新公司,按试剂说明书步骤操作。
2 结果
2.1 例1 巨检(图a) 脾脏切除标本一个,大小为20cm×11cm×2cm 。沿脾门切开,切面灰红、质中,见出血区域。例2(图b) 巨检 脾脏组织一个,大小为20cm×15cm×10cm 。沿脾门切开,切面灰红灰黄、质中,呈多结节状。例3 巨检 肋骨一段,带少许皮肤。肋骨长为9cm,最大直径3cm。切开切面灰红、质硬,伴有骨质破坏。例4 巨检 组织两块,大小共为5cm×4cm×2.5cm,切开切面灰白灰黄、质中。光镜(图c-f)肿瘤细胞排列成条索状或巢团状,具有内皮细胞分化特点。瘤细胞为含丰富胞质的上皮样细胞,内见明显空泡且含有红细胞。细胞核圆形呈空泡状,核分裂象少见。间质为淡蓝色软骨样或深红色玻璃样,可见浆细胞、淋巴细胞、嗜酸性粒细胞等炎细胞浸润。免疫组化(图g-i)肿瘤细胞CD34(+)、CD31(+)、FⅧ(+)、Ki-67(+,<10%)。
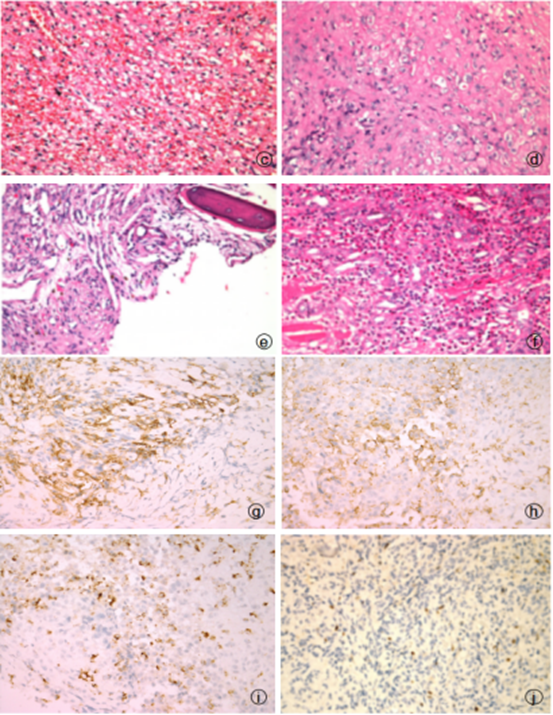
图c 例1脾脏,肿瘤细胞胞浆丰富,呈空泡状,内含红细胞 图d 例2脾脏,肿瘤具有深红色玻璃样间质 图e 例3肋骨,可见骨组织及胞浆丰富、内含空泡的上皮样细胞 图f 例4颏部软组织,间质可见浆细胞、淋巴细胞、嗜酸性粒细胞等炎细胞浸润 图g 肿瘤细胞胞质CD34(+),Max Vision法 图h 肿瘤细胞胞质 CD31(+),Max Vision法 图i 肿瘤细胞胞质FⅧ(+),Max Vision法 图j 肿瘤细胞胞核 Ki-67(+,<10%),Max Vision法
2.2 病理诊断 上皮样血管内皮细胞瘤
3 讨论
3.1临床表现与治疗
上皮样血管内皮细胞瘤 ( epithelioid haemangioendothelioma,EHE) 是一种具有转移潜能的中间型血管源性肿瘤,一般发生于肝脏、皮肤、骨、肺等部位,可见于任何年龄组,女性较多见[3-5]。肿瘤多为位于表浅或深部软组织的结节,因起源于血管而易于伴发水肿或血栓性静脉炎,导致组织变性坏死。发生于肝、脾等实质性脏器者往往以占位性病变为主,发生于骨时常伴有骨质溶骨性破坏而易于骨折[6,10]。临床上EHE的治疗手段为手术切除、辅以放疗。早期患者经手术扩大切除后辅以放疗较仅手术切除治疗预后好。对于不可切除病灶的晚期患者可选用放疗治疗[7,8]。目前WHO分类已将EHE定义为中间型血管源性肿瘤,这提示部分患者在治疗后仍有复发转移的风险。因此EHE预后与病理组织学关联的研究显得尤为重要。----等发现,EHE预后与发生部位有关,表浅部位较内部脏器预后好,而与肿瘤体积大小、组织学特点无关。-----等研究却认为EHE预后与肿瘤大小、核分裂像、浸润深度和有否累及周围脏器等因素有关(核分裂像>3个/50HPF、直径>3cm 的EHE患者预后较差)[9-13]。
3. 2 病理学及分子遗传学
EHE的病理组织学特点为:肿瘤细胞起源于血管,早期使血管受累扩张膨胀,压迫周围软组织。细胞排列成条索状或巢团状,具有内皮细胞分化特点。瘤细胞为含丰富胞质的上皮样细胞,内见明显空泡且含有红细胞。细胞核圆形,核分裂象少见。间质为淡蓝色软骨样或深红色玻璃样,可见浆细胞、淋巴细胞、嗜酸性粒细胞等炎细胞浸润[14-16]。免疫组化内皮细胞标记物 CD31、CD34、FⅧ阳性。25%-30%的病例可散在表达上皮标记物 CK 、EMA,少数细胞可具有轻度异型性[19-20]。通过电镜观察可发现,肿瘤细胞表面有吞饮泡,可有weibel-palade小体,细胞内含有丰富的中间丝。EHE发生与基因异常表达密切相关,现已发现的染色体异常:1号及3号染色体重排t(1;3)(p36.3;q25)、染色体12q12-13 与12q14-21的扩增及11q21的缺失等,因此在病理形态学上难以鉴别或免疫组化标记判读不确定时,分子遗传学检查也作为一项诊断依据[19,23]。
3,3鉴别诊断
(1)上皮样血管肉瘤 肿瘤细胞胞浆丰富,内皮细胞不典型,核分裂像较EHE显著增多,可形成血窦样结构,肿瘤内含有实性瘤细胞区并可见坏死。
(2)上皮样肉瘤 多发于远端肢体,可见嗜酸性上皮样和梭形细胞增生。细胞核轻度异型,肿瘤内有多结节组成,中心为坏死物,周边有栅栏状排列细胞,形成假肉芽肿性病变。
(3) 转移性腺癌 巢团状的上皮样肿瘤细胞易被误诊为转移性腺癌,特别是在影像学也支持转移癌可能时。病理学鉴别点则在于腺癌细胞可有腺样分化区域且异型性更明显,核分裂象多见,浸润性生长。免疫组化腺癌细胞上皮性标记阳性,而内皮性标记(CD34、CD31)等阴性。
综上所述,EHE是一种具有转移潜能的中间型血管源性肿瘤,因此病理学诊断中不仅要熟悉掌握其组织学特点、临床及影像学表现,同时也要做好与其他血管源性肿瘤的鉴别。我院诊治的4例EHE病例均为女性患者,年龄30~62岁。2例发生于脾脏,1例发生于骨组织,1例发生于软组织。我们在搜集病例、撰写文章过程中思考:是否可以从分子表型将EHE区分开来,为其预后提供参考。我们统计EHE发生部位、肿瘤体积大小、核分裂像及浸润程度,并做好密切的病例术后随访方案,希望为下一步研究做准备。
参考文献:
[1]Zaragoza-Herrera A, Morales-Baños DR, Velasco-Ramos P,et al. Case report: Orbital epithelioid haemangioendothelioma. Arch Soc Esp Oftalmol. 2016 Apr 28.
[2].Lezama-Urtecho C,Álvarez-Sánchez L. [Primary cardiac hemangioendothelioma: early diagnosis and surgical resection]. Rev Med Inst Mex Seguro Soc. 2016 May-Jun;54(3):392-6.
[3]Ciliberti MP, Caponio R, Pascali A,et al. A rare case of intravascular epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the cephalic vein treated with surgery and postoperative radiation therapy: a case report and review of the literature. Journal of Medical Case Reports. 2015;9:91.
[4]Singh A, Sood N, Puri HK,et al. S Primary Hepatic Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma: Diagnostic Dilemmas in Cytology and Histology. J Oncol Pract. 2016 Apr;12(4):394-6.
[5]Park SM, Kim HS, Ko HC, Kim BS, Kim MB, Mun JH. Cutaneous epithelioid
hemangioendothelioma treated with Mohs micrographic surgery. Int J Dermatol. 2016 Apr 7.
[6]Ciliberti, Maria Paola etal. “A Rare Case of Intravascular Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma of the Cephalic Vein Treated with Surgery and Postoperative Radiation Therapy: A Case Report and Review of the Literature.”Journal of Medical Case Reports 9 (2015): 91. PMC. Web. 3 Oct. 2016.
[7] Ciliberti, M. P., Caponio, R., Pascali,et al (2015). A rare case of intravascular epithelioid hemangioendothelioma of the cephalic vein treated with surgery and postoperative radiation therapy: a case report and review of the literature. Journal of Medical Case Reports, 9, 91.
[8]Barger J, Tanweer O, Liechty B,et al Suprasellar epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: Case report and review of the literature. Surgical Neurology International. 2016;7(Suppl 23):S596-S602.
[9]Sardaro, Angela et al. “Pulmonary Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma Presenting with Vertebral Metastases: A Case Report.” Journal of Medical Case Reports 8 (2014): 201. PMC. Web. 3 Oct. 2016.
[10]Bardoscia, L., Petruzzelli, M. F., Nikolaou, A., Detti, B., & Angelelli, G. (2014). Pulmonary epithelioid hemangioendothelioma presenting with vertebral metastases: a case report. Journal of Medical Case Reports, 8, 201. http://doi.org/10.1186/1752-1947-8-201
[11]ZHAO XY, RAKHDA MIA, HABIB S, et al. Hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: A comparison of Western and Chinese methods with respect to diagnosis, treatment and outcome. Oncology Letters. 2014;7(4):977-983.
[12]Semenisty, V., Naroditsky, I., Keidar, et al. (2015). Pazopanib for metastatic pulmonary epithelioid hemangioendothelioma—a suitable treatment option: case report and review of anti-angiogenic treatment options. BMC Cancer, 15, 402
[13]Liu Q, Miao J, Lian K, et al Multicentric Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma Involving the Same Lower Extremity: A Case Report and Review of Literature. International Journal of Medical Sciences. 2011;8(7):558-563.
[14]Liu, Qingjun et al. “Multicentric Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma Involving the Same Lower Extremity: A Case Report and Review of Literature.” International Journal of Medical Sciences 8.7 (2011): 558–563.
[15]Liu, Q., Miao, J., Lian, K., et al. (2011). Multicentric Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma Involving the Same Lower Extremity: A Case Report and Review of Literature. International Journal of Medical Sciences, 8(7), 558–563.
[16]Jolissaint JS, Kilbourne SK, LaFortune K, et al. Benign metastasizing leiomyomatosis (BML): A rare cause of cavitary and cystic pulmonary nodules. Respiratory Medicine Case Reports. 2015;16:122-124.
[17]McCulloch M, Russin M, Nachat A. Recurrence of Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma during Pregnancy: Case Report and Systematic Review. The Permanente Journal. 2016;20(3):84-89.
[18]McCulloch, Michael, Michael Russin, et al “Recurrence of Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma during Pregnancy: Case Report and Systematic Review.” The Permanente Journal 20.3 (2016): 84–89.
[19]McCulloch, M., Russin, M., & Nachat, A. (2016). Recurrence of Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma during Pregnancy: Case Report and Systematic Review. The Permanente Journal, 20(3), 84–89.
[20]Semenisty, Valeriya et al. “Pazopanib for Metastatic Pulmonary Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma—a Suitable Treatment Option: Case Report and Review of Anti-Angiogenic Treatment Options.” BMC Cancer 15 (2015): 402.
[21]ZHAO, XIN YAN et al. “Hepatic Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma: A Comparison of Western and Chinese Methods with Respect to Diagnosis, Treatment and Outcome.” Oncology Letters 7.4 (2014): 977–983.
[22]ZHAO,X. Y., RAKHDA, M. I. A., et al. (2014). Hepatic epithelioid hemangioendothelioma: A comparison of Western and Chinese methods with respect to diagnosis, treatment and outcome. Oncology Letters, 7(4), 977–983.
[23]SHAO, JINCHEN, and JIE ZHANG. “Clinicopathological Characteristics of Pulmonary Epithelioid Hemangioendothelioma: A Report of Four Cases and Review of the Literature.” Oncology Letters 8.6 (2014): 2517–2522.













共0条评论